
Ansible will ask for root password, create a system admins group with access to sudo, create an user account based on your current user, copy your ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub to your new account, and add it to the admins group.įrom now you can use Ansible through your user account using sudo. Run Ansible with: ansible-playbook -k -l host init.yml.
Lineinfile: "dest=/etc/sudoers.d/admins state=present create=yes regexp='^%admins' line='%admins ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: SETENV: ALL' owner=root group=root mode=0440"
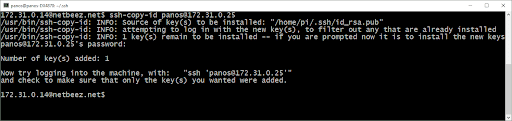
Ansible ssh copy id without password install#
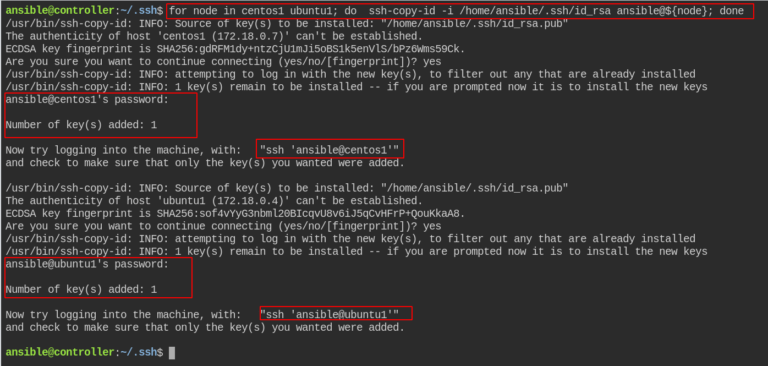
name: INIT | Install sudoers file for admin accounts name: INIT | Install ssh public key from current accountĪuthorized_key: user=$ssh_user key="$FILE(~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)" If the ansible user does not exist on the destination machine, it should be created. name: INIT | Make sure essential software is installedĪpt: pkg=$item state=latest install_recommends=no Try to use ssh-copy-id and also specify the user on which you copy the credentials. User: name=$ssh_user state=present shell=/bin/bash groups=admins name: INIT | Create admin account from current user Group: name=admins system=yes state=present
After installation, default password for root account will be debian and you will be forced to change it upon first login. If you want to test it on a VM, you can run Debian installer with boot parameter url= - installer will download a preseed file with python and python-apt packages selected (among others).
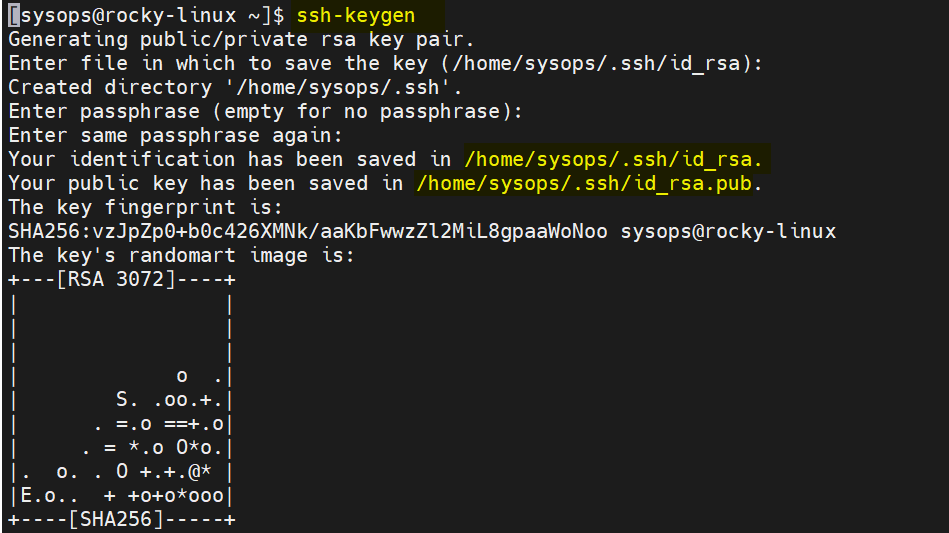
Host needs to have python and python-apt packages installed for this playbook to work out of the box. Here's a method I use to provision new Debian hosts without known ssh keys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
